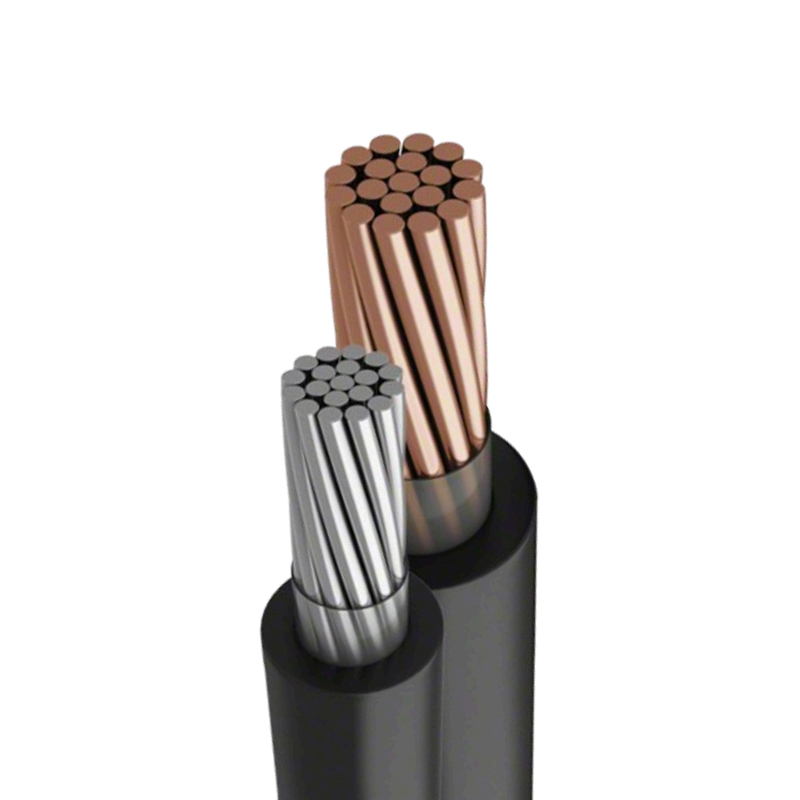
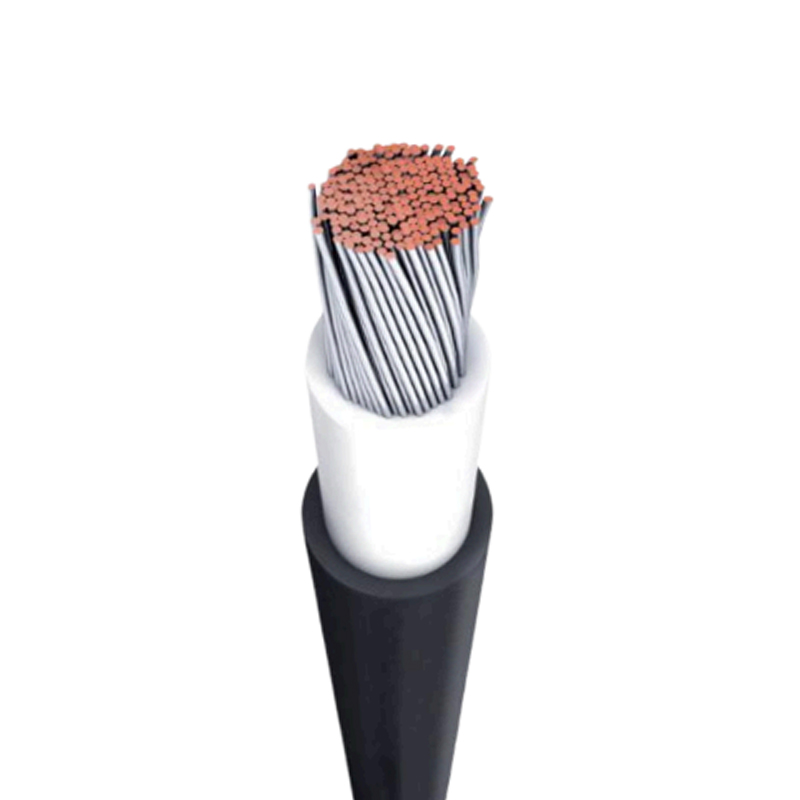
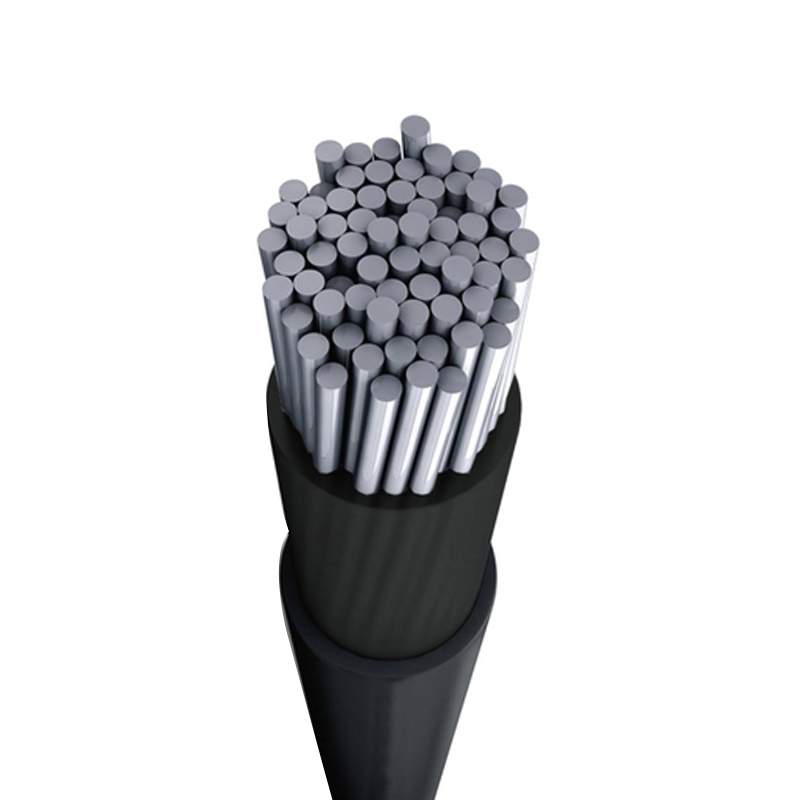
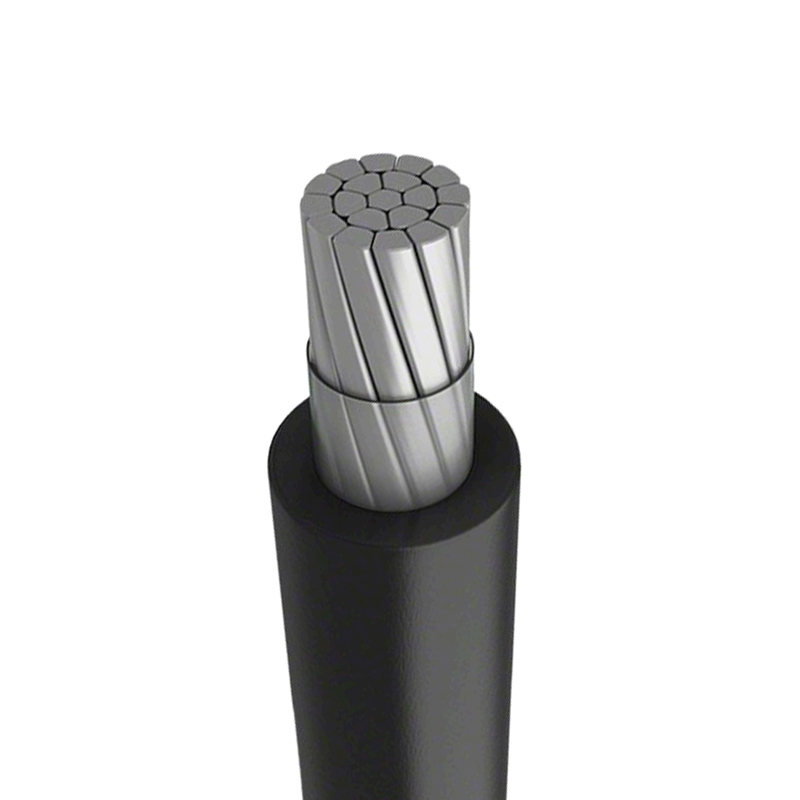
Solar Cables Manufacturers
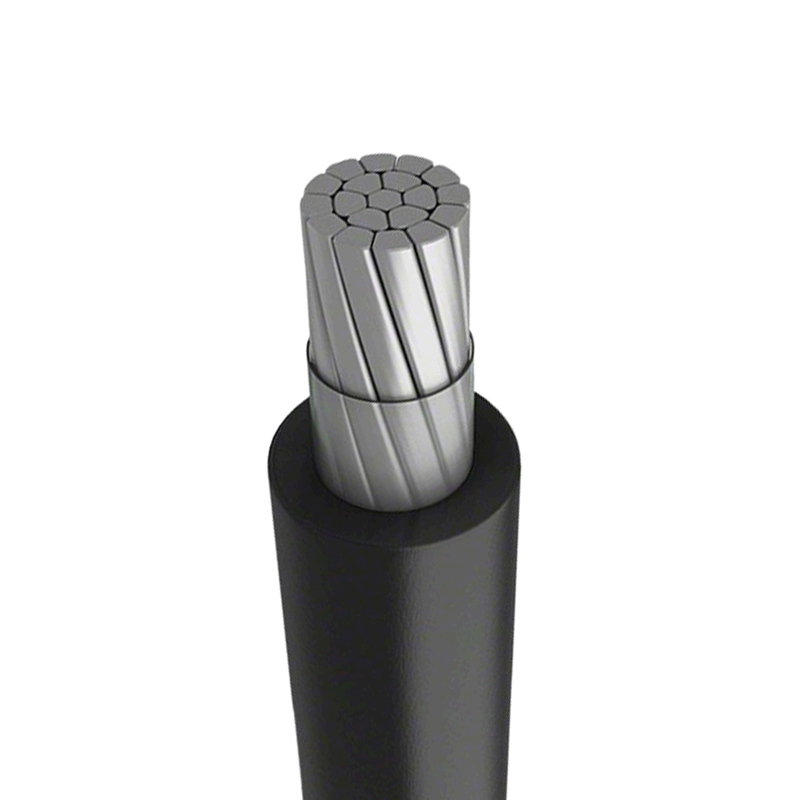
Solar cables are critical conductors specifically designed for photovoltaic (PV) power generation systems. Unlike ordinary cables, they must be able to withstand extremely harsh outdoor conditions, such as intense UV radiation, high and low temperatures, rain, snow, and ozone erosion. Additionally, the sheathing material of solar cables has excellent mechanical strength and abrasion resistance, allowing it to withstand the squeezing, bending, and tensile stresses that may be encountered during installation and maintenance.
Selecting the appropriate cable size requires a comprehensive consideration of current, voltage level, and cable length to ensure that voltage drop is within an acceptable range. Internationally, the production and application of solar cables are subject to strict certification and standard regulation by authoritative bodies such as TÜV, UL, and IEC. Certifications like TÜV PV1-F and UL 4703 are important benchmarks for measuring cable quality and reliability, ensuring that solar cables can serve global PV power plants efficiently, safely, and reliably.

About Us
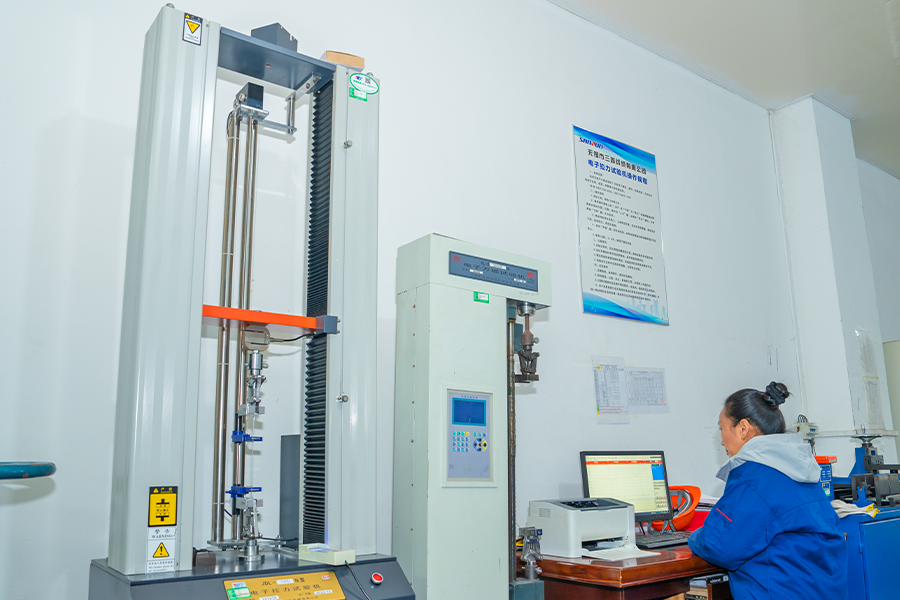
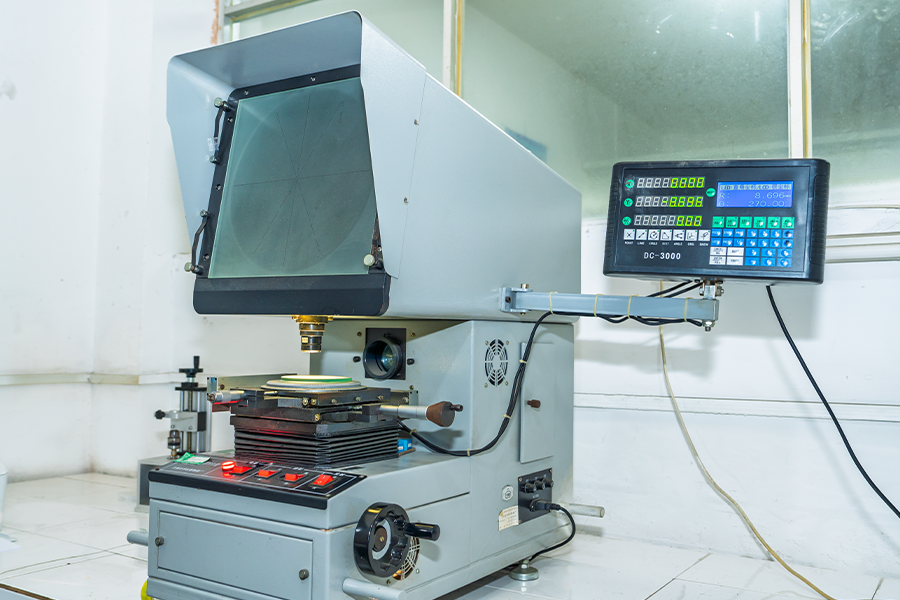
Factory Tour
Contact us now
Latest Enterprise and Industry News
-

 2026-03-02
2026-03-02 Industry News
Industry News -

 2026-02-24
2026-02-24 Industry News
Industry News -

 2026-02-18
2026-02-18 Industry News
Industry News
industry knowledge
Understanding the Importance of Solar Cable Sheath Materials
The outermost layer of a solar photovoltaic (PV) cable, the sheath, is crucial for protecting the internal conductors and insulation from the harsh operational environment. Unlike general-purpose cables, solar cables are exposed to extreme conditions outdoors, necessitating specialized materials. We at Wuxi Sanxin Cable Co., Ltd. understand that the choice of sheath material directly impacts the cable's longevity and the overall system's safety and performance.
Key Performance Factors for Solar Cable Sheaths
- UV and Ozone Resistance: Prolonged exposure to sunlight can degrade standard polymer materials. A good solar cable sheath must exhibit excellent resistance to UV radiation and ozone to prevent cracking and material breakdown.
- Temperature Extremes: PV installations operate in wide temperature ranges, from freezing winters to scorching summers. The sheath material must maintain its mechanical and electrical integrity across these extremes.
- Water and Moisture Resistance: The cable must resist moisture ingress to prevent corrosion of the conductor and maintain the integrity of the insulation, especially in humid or rainy climates.
- Flame Retardancy and Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH): In the event of a fire, the cable should resist flame propagation and emit minimal smoke and toxic fumes. This is a critical safety feature, and it's a standard we uphold in our flame retardant and fire resistant cables.
- Abrasion and Tear Resistance: During installation and throughout the cable's service life, it may be subject to mechanical stresses. A durable sheath resists abrasion and tearing, ensuring continuous protection.
Understanding the Differences in Solar Cable Insulation and Sheath Materials
While both the insulation and the sheath protect the conductor, they serve distinct purposes and are often made of different materials, though both must be highly specialized for PV applications. The insulation directly surrounds the conductor and is primarily responsible for electrical isolation, while the sheath is the outermost protective layer.
Common Material Comparison for Solar Cables
Materials like Cross-Linked Polyolefin (XLPO) are commonly used for both insulation and sheathing in high-quality solar cables due to their superior performance characteristics compared to standard PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride). These specialized materials are essential for achieving the required 25-year lifespan of a PV system.
| Material Type | Key Advantage | Typical Application |
| XLPO (Cross-Linked Polyolefin) | Excellent UV, weather, and thermal resistance; LSZH properties. | High-performance insulation and sheathing for DC PV cables. |
| EPR (Ethylene Propylene Rubber) | Excellent flexibility and high-temperature performance. | Insulation for flexible and high-temperature cables. |
| PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) | Cost-effective; generally used for less demanding, standard applications (not ideal for long-term outdoor PV). | Standard general wiring, not recommended for direct outdoor solar use. |
Practical Considerations for Solar Cable Sizing and Voltage Drop
Properly sizing the solar cables is a critical engineering step often overlooked, which can lead to significant energy losses and reduced system efficiency. This goes beyond simple ampacity; the allowable voltage drop is the key determining factor for DC cables in a PV array.
Calculating Allowable Voltage Drop
The objective is to choose a conductor cross-sectional area that keeps the voltage drop below a specified threshold, typically 1% to 3% of the system voltage. The calculation involves the cable's resistance, the length of the run, and the current flowing through it.
Where:
- L is the one-way length of the cable (in meters).
- I is the maximum current (in Amperes).
- ρ is the resistivity of the conductor material (e.g., 0.0172Ω⋅mm2/m for copper).
- A is the conductor cross-sectional area (in mm2), which is the variable you solve for.
When the voltage drop is excessive, it results in power loss in the form of heat, which is a direct reduction in the energy delivered to the inverter. A seemingly small increase in cable gauge can dramatically improve efficiency over the system's life. We engineer our specialty cables with optimal conductivity to minimize these losses, delivering true value.


 Language
Language
 English
English عربى
عربى